USE CASES
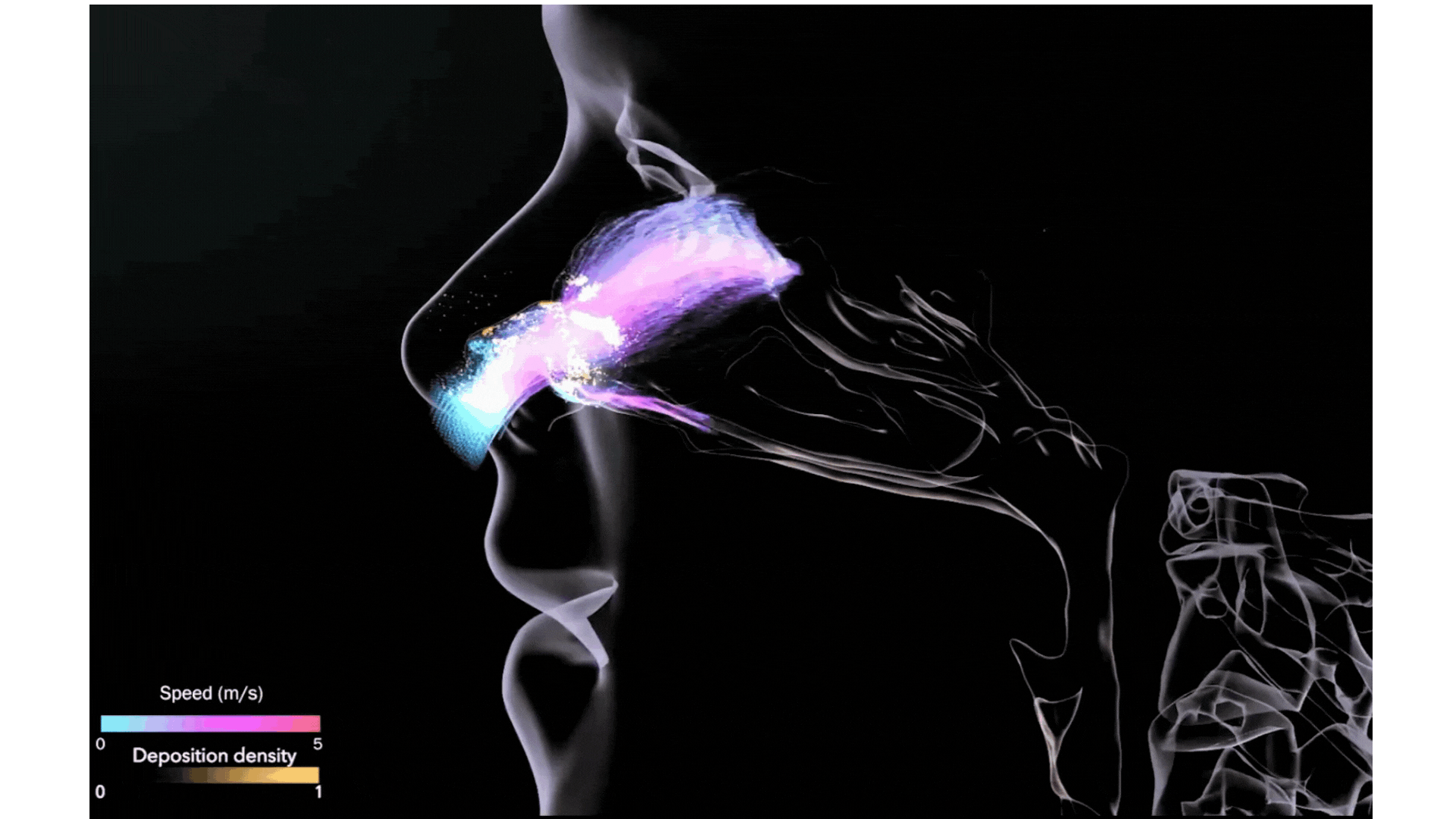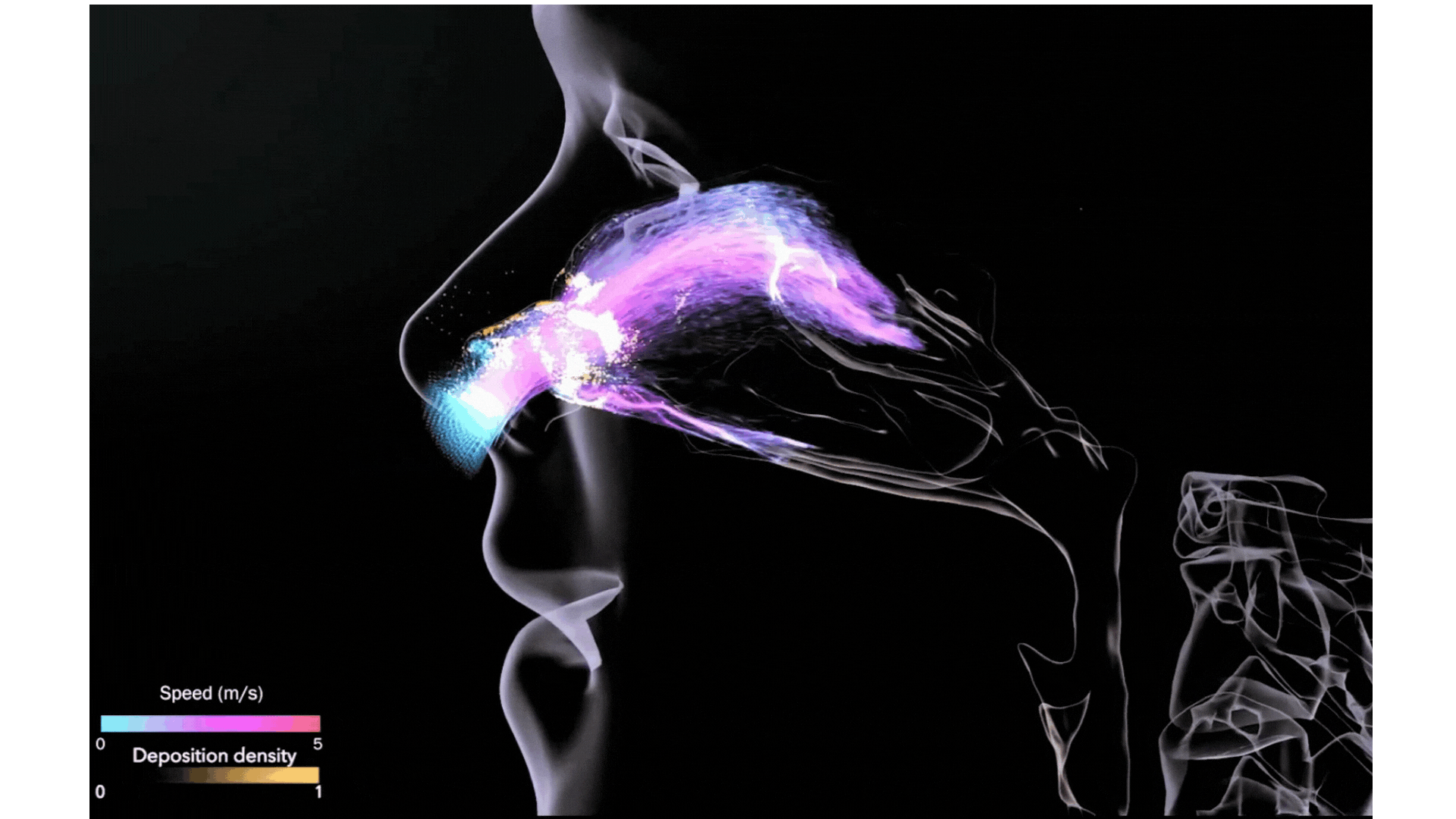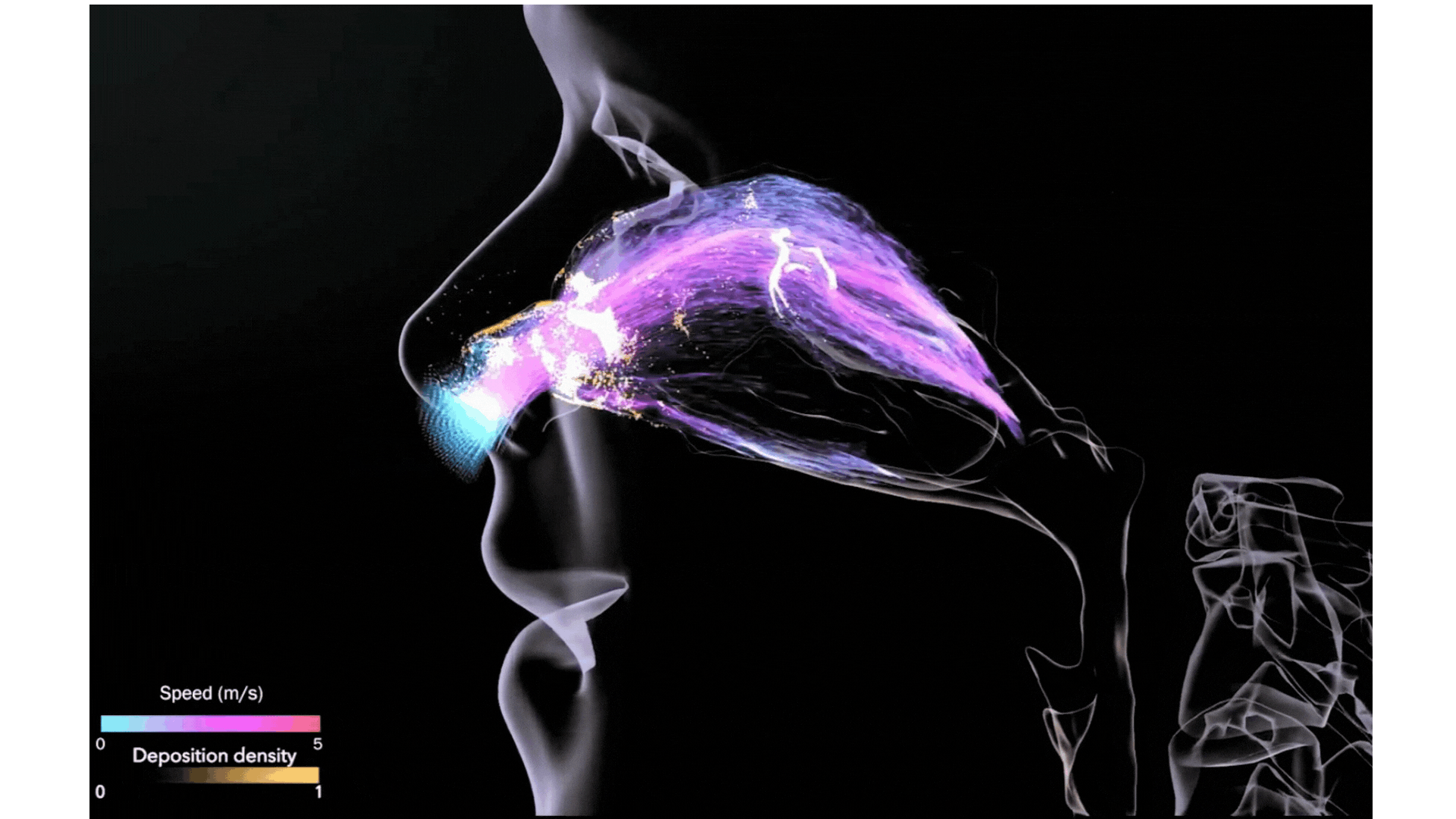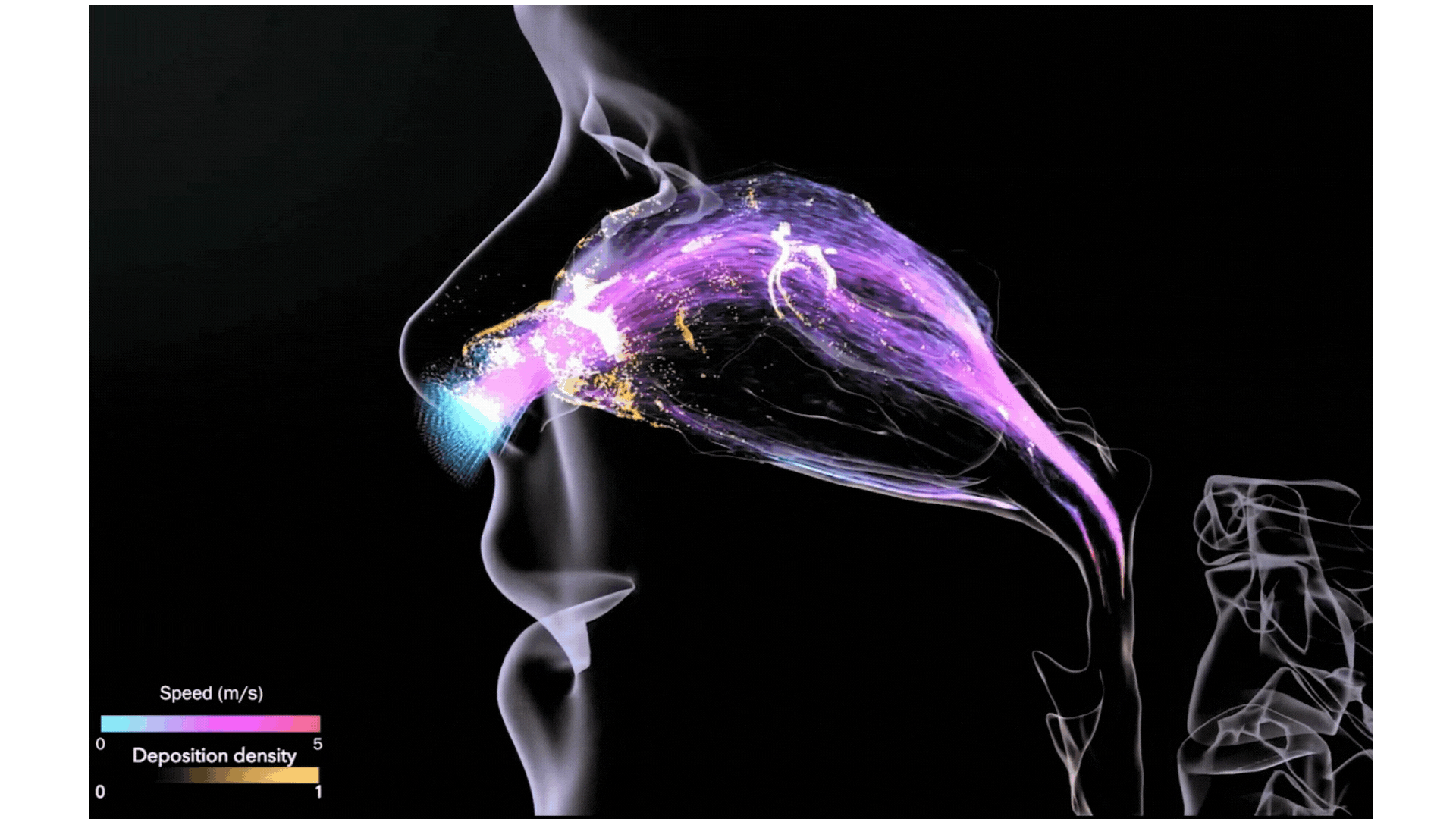
Illustration Courtesy of BSC Data Visualization Group
HEALTH CRISIS USE CASE
CREXDATA aims to provide a comprehensive picture of the dynamics and outcomes of emergent health crises, as well as the potential impacts of different strategies and policies. The consortium also works towards allowing end-users to access and visualise various data-driven outcomes, such as case reports, hospitalisations, deaths, mobility patterns and environmental factors.
CREXDATA’s tools enable decision-makers to:
- Simulate epidemic scenarios: Using tools like EpiSim.jl, we model the spread of infectious diseases, considering factors like mobility patterns, vaccination coverage, and waning immunity.
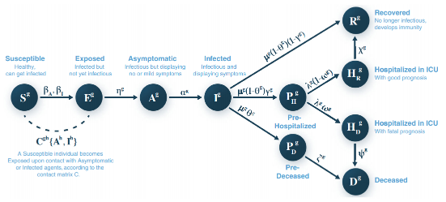
- Optimize interventions: Our simulations help identify the best strategies, such as lockdowns or vaccination campaigns, to minimize transmission, hospitalizations, and fatalities.
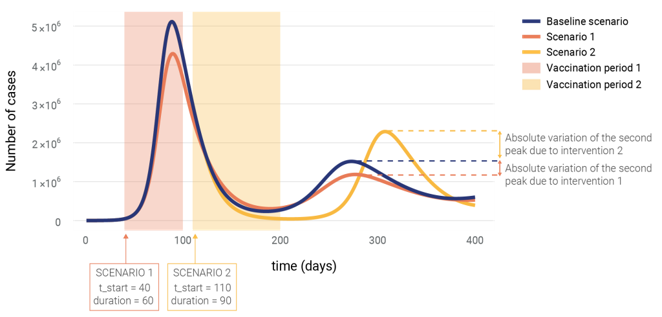
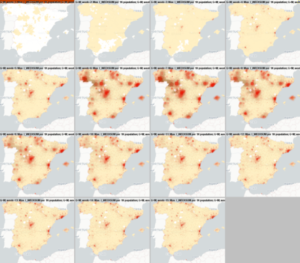
- Visualize data effectively: Through integrated workflows, we offer clear insights that reduce complexity and enhance decision-making during health crises.
Modelling health crisis
Crexdata has focused on two main scenarios for modelling health crisis: epidemiological modelling and multiscale lung infection modelling. Our models have already been applied to study COVID-19 spread in Spain, evaluating the impact of mobility restrictions and vaccination campaigns. This ensures our tools are grounded in real-world data and ready to address future crises.
-
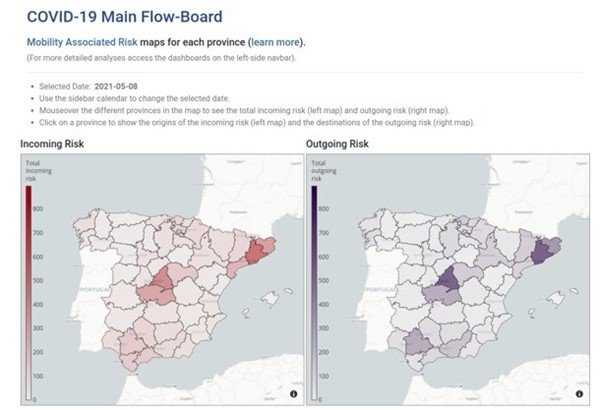
Epidemiological models
Mechanistic epidemiological models will be used to build a toolbox that aims to have digital twins that mimic the movement and infection of populations. These models become even more relevant when dealing with the spread of an unknown infectious pathogen, such as SARS- CoV-2, as it allows us to evaluate and monitor early warning mechanisms and indicators during the time when non- pharmacological interventions are necessary.
-
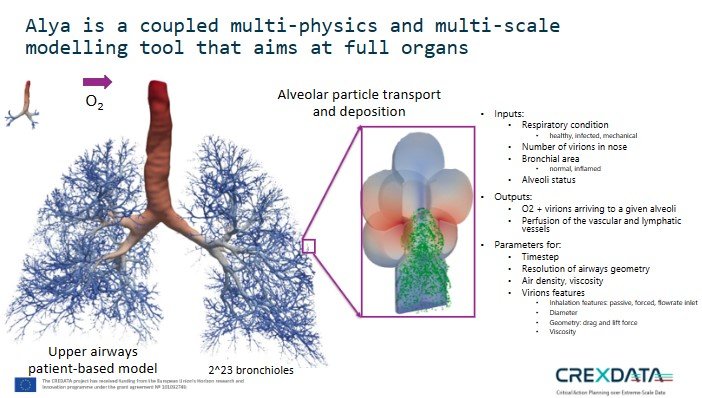
Multiscale models
Mechanistic multiscale models will be used to build a toolbox aimed at having a digital twin for the treatment of patients. CREXDATA will build a multiscale, multicellular, spatiotemporal model of lung tissue infected by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. This COVID19 infection simulator will be a first version of a digital twin that will allow testing of different interventions in patients, allow them to receive treatments, such as vaccines and virus-infection-targeting drugs.
Read more about this case:
- From Movement to Infection: Deciphering COVID-19 Transmission via Transfer Entropy
- Digital Twin Models of the Human Respiratory System
- A Digital Twin of COVID-19 Infected Lungs Allows for Personalized, Interactive Clinical Interventions
- New AI-Driven Simulation Tools Set to Revolutionize Pandemic Response
- Integrating Agent-Based Models and HPC Workflows: A New Multiscale Approach to Simulating Lung Infection Dynamics
- Pioneering Data-Driven Solutions for Global Health Preparedness in the European Union
- Open-Source Epidemic Simulations with Epi-Sim and CREXDATA
- Extreme Scale Big Data Analytics Towards Battling Cancer- Presentation at EMBO WS
- Optimizing Outbreak Response: How Mathematical Models Inform Real-World Decision Making