Members of the TUC CREXDATA team have been driving major advances in optimizing the deployment of extreme-scale analytics workflows across the cloud–edge continuum. At its core, the team is tackling a pressing challenge in modern computing: how to translate high-level application workflows into efficient, real-world execution plans that run across complex, heterogeneous networks.
To address this, researchers have introduced two powerful new tools, the APEROL optimization suite and the DAG* algorithm. APEROL is a suite of algorithms that rapidly explore millions of candidate execution plans by leveraging parallelism, making it possible to navigate vast search spaces that would otherwise be computationally prohibitive. DAG*, on the other hand, brings an A*-like pruning on the search space to significantly limit optimization time with the important feature of guaranteeing latency-optimal physical plans.
Both approaches are designed not only for speed, but also for adaptability. They factor in runtime conditions, helping workflows maintain high performance even as networks evolve or workloads shift. APEROL, running on standard hardware, can rapidly examine up to 2 million physical plans per second, while DAG* is able to cut down search spaces by two to three orders of magnitude while swiftly providing latency-optimal solutions.
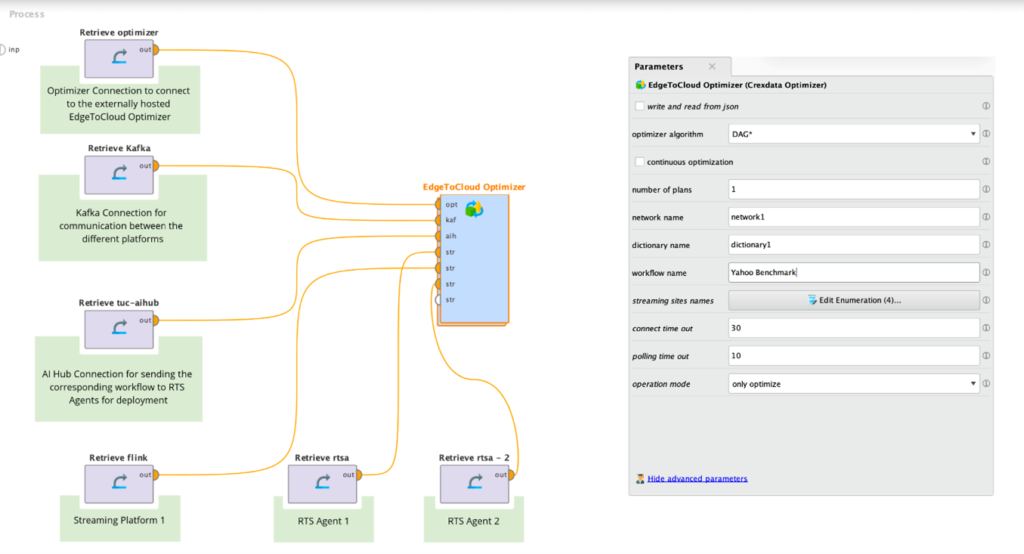
Figure 1: Optimizer Configuration
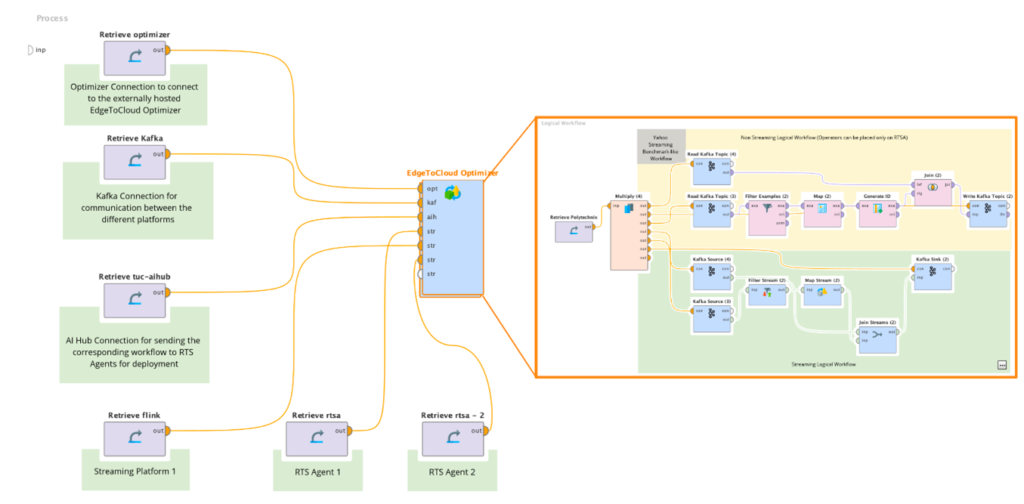
Figure 2: Designed Logical Workflow
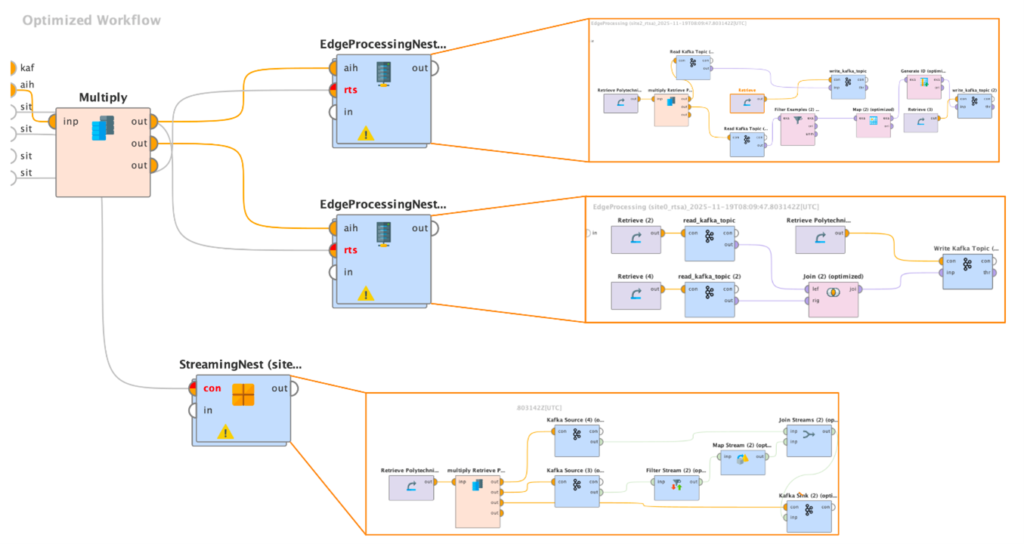
Figure 3: Optimized Physical Workflow on Devices
Latest developments
Under the leadership of TUC, with contributions from RM, MT, and DRZ, APEROL (initially including Exhaustive Search with Counting (ESQ), Random Sampling Search (RSS), Greedy algorithms) has been enhanced with two new algorithms, Exhaustive Search with a Queue (ESQ) and a Pareto-guided Heuristic algorithm, further strengthening its versatility across diverse network environments. Alongside this, DAG* has been introduced as a non-parallel A*-alike algorithm that guarantees optimality for end-to-end latency via efficient pruning.
The team has carried out one of the most extensive evaluation campaigns in the field to date, testing the algorithms on both simulated and real-world environments of varying sizes and heterogeneity. The setup included six workflows across two established benchmarks, more than ten network configurations, and comparisons against two candidate state-of-the-art approaches. The results consistently confirmed the effectiveness and complementarity of the newly developed algorithm in all the aforementioned setups.
Key contributions
- APEROL optimization suite (ESC, RSS, Greedy, ESQ, Heuristic) supporting multi-objective optimization over throughput, latency, communication cost, and migration cost, using parallel workers to explore the GoP.
- DAG*, an A*-based placement algorithm that progressively constructs partial physical plans in topological order, using an admissible heuristic to prune the search space while guaranteeing latency-optimal solutions.
- A comprehensive experimental methodology, including plan-cost improvements, execution-time metrics, benchmarks against state-of-the-art methods (e.g., GOVERNOR and SPRING-RELAX), and full scalability analyses.
- Full integration of the optimizer via an optimization service in the EdgeToCloud Extension, integrated into the Altair AI Studio.
Deliverables
Algorithms & evaluation: an extended APEROL suite (including ESQ/Heuristic) and DAG*, along with extensive benchmarking results (Yahoo, RIoT) on simulated and real (FITIoT) testbed setups. The deliverable reports detailed rankings/trade-offs (plan cost or latency vs. algorithm execution time) and scalability observations such as high plan-examination rates when batching is enabled.
Datasets
- Yahoo Benchmark: standard stream-analytics workflow (selection/projection/join/window/aggregation). RIoT benchmark: four smart-city workflows—TRAIN, PRED, ETL, STATS—with 8–11 operators each.
- Network setups: FIT IoT-LAB Grenoble site (up to 194 devices) for real measurements; simulated networks of sizes {7, 15, 31, 127, 1023, 2047} using iFogSim, in heterogeneous (mixed edge hardware) and homogeneous (Raspberry-Pi-class) configurations.
- Software available in: https://github.com/altairengineering/crexdata-public/tree/main/WP4/optimization