The Technical University of Crete (TUC) is leading a critical advancement in decentralized artificial intelligence as part of the CREXDATA project. Tasked with heading Federated Machine Learning, TUC is developing novel algorithms designed to make large-scale AI training more efficient, particularly for high-stakes weather crisis scenarios.
By moving away from continuous or “data-oblivious” communication, TUC’s research ensures that dispersed devices only communicate when the global model is likely to have changed significantly, drastically reducing network strain.
Breakthrough Algorithms: FDA and FDA-Opt
A core contribution of TUC is the development of two primary algorithms that cater to different network environments:
- Federated Dynamic Averaging (FDA): Focused on the cross-silo setting, this algorithm federates a small number of data silos. It achieves high-quality performance while delivering an order-of-magnitude decrease in communication overhead.
- FDA-Opt: Designed for cross-device settings involving massive numbers of low-end devices, this algorithm dynamically adapts the learning process to the specific characteristics of local data found on individual devices.
These methods represent a significant leap in efficiency over existing federated learning techniques.
Advanced Infrastructure and Simulation
To bridge the gap between theory and real-world deployment, TUC has developed a comprehensive software stack for the CREXDATA architecture:
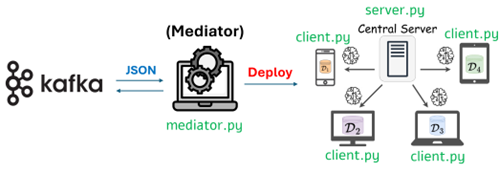
- Federated Learning Operator: This tool supports both FDA and FDA-Opt. It is designed for flexibility, running as a standalone service or integrated directly into RapidMiner workflows.
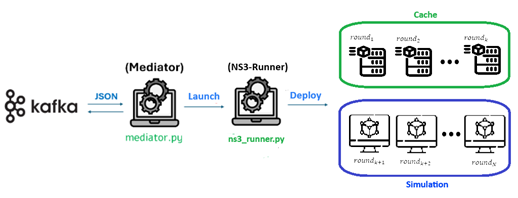
- FL Network Simulator: Built upon the industry-standard NS3 simulator, this tool allows researchers to model unpredictable network conditions. The insights gained are used to fine-tune the hyper-parameters of FL jobs within the operator.
Real-Time Emergency Awareness via Adaptive NeRFs
TUC’s contributions extend into specialized computer vision through an adaptive NeRF (Neural Radiance Fields) framework. This technology is specifically tailored for city-scale emergency awareness.
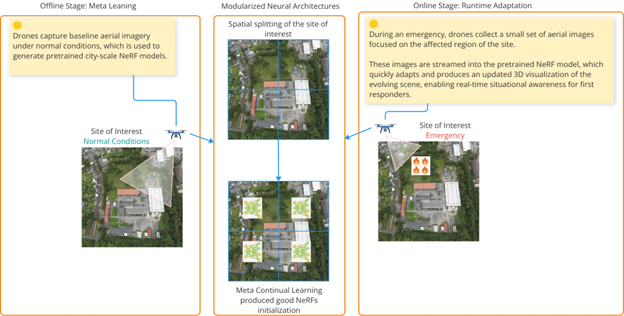
- Meta-Continual Learning: The framework uses drone-acquired streaming video to quickly adapt NeRF models to evolving scenes.
- Operational Flow: Drones capture baseline imagery under normal conditions to create pre-trained models. During an emergency, they stream a small set of images from the affected area to update the 3D visualization in real-time for first responders.
Technical Access and Collaboration
This task involves collaboration with partners including RM, NCSR, and BSC. Developers and researchers can access the technologies and implementations through the project’s public repository.