As extreme weather events become more frequent and severe, the ability to extract actionable intelligence from the noise of social media is becoming a critical asset for emergency responders.
The CREXDATA EU project has announced a significant milestone in this domain with the release of a new text mining toolkit designed to handle crisis data in real time. Led by the Barcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC), Task 4.5 delivers a robust, multilingual system capable of crawling, classifying, and extracting vital information from platforms like X (formerly Twitter) to support decision-making during wildfires and floods.
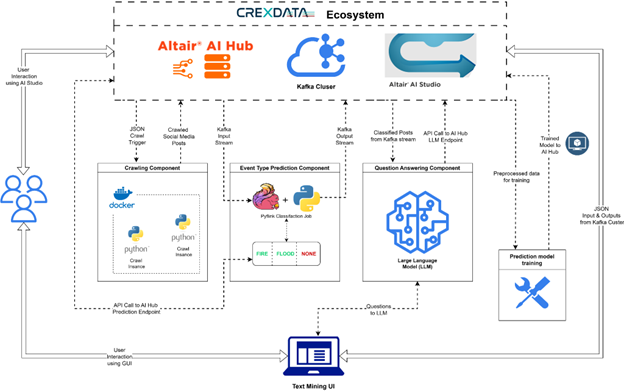
CREXDATA Ecosystem
The Challenge: Making Sense of Noise
During a crisis, social media explodes with data. However, this data is often unstructured, filled with jargon, and multilingual. The primary objective of the CREXDATA text mining task was to build a system that supports decision-making by extracting clear signals from this chaotic “social media ecosystem”.
Under the Hood: Multilingual Language Models (MLLM)
The backbone of the new system is a specialized Multilingual Language Model (MLLM). Unlike generic models, this MLLM has been pre-trained on massive volumes of social media text to master the specific nuances of online communication, including abbreviations, emoticons, and folksonomy traits.
Key technical innovations include:
- Zero-Shot Learning via Prompting: Recognizing that crisis events are diverse, the team utilized prompting techniques to allow the model to handle new types of events without extensive retraining —a capability known as zero-shot learning.
- Efficiency & Distillation: Two versions of the model were developed: a full-finetuned model for maximum accuracy and a distilled model optimized for faster inference and efficiency, ensuring the system requires fewer resources to operate online.
- Real-Time Pipeline: Once fine-tuned, the models operate online to process events as they unfold.
Architecture: From Crawling to QA
The toolkit introduces a modular architecture that ties together data collection and analysis:
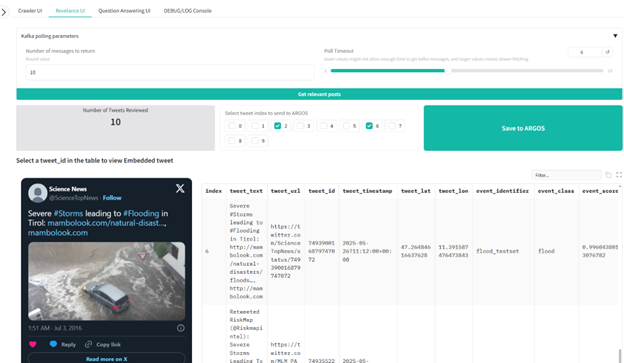
- Crawler Component: A Dockerized component continuously collects posts from Twitter/X.
- Relevance Prediction: A Pyflink classification job utilizes the MLLM to instantly filter posts, tagging them as relevant (e.g., “FIRE”, “FLOOD”) or irrelevant.
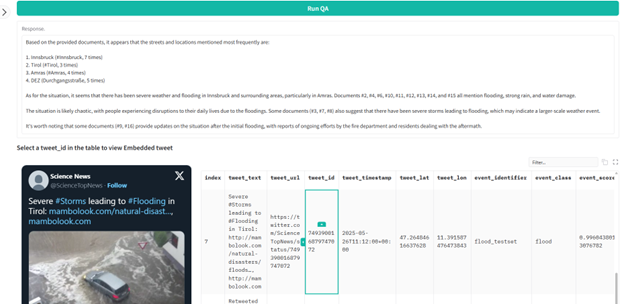
- Question Answering (QA): A novel component allows responders to run custom queries against an LLM to extract specific details—such as street names or damage reports—from the most relevant posts.
- GUI: A specialized Text Mining User Interface brings these elements together, visualizing tweet locations and event scores for operators.
Battle-Tested on Recent Disasters
To validate the system, the consortium curated massive datasets comprising over 450,000 real tweets in English, Spanish, Catalan, and German. These datasets cover historical and recent major incidents, including the Valencia flash floods of 2024 and the Los Angeles wildfires of 2025. An additional 37,000 synthetically generated tweets were used to augment training data.
Outlook
The deployed system is designed for continuous improvement, capable of on-line learning to adapt as new data arrives during an unfolding crisis. This release marks a step forward in CREXDATA’s mission to leverage extreme-scale data for critical action planning.